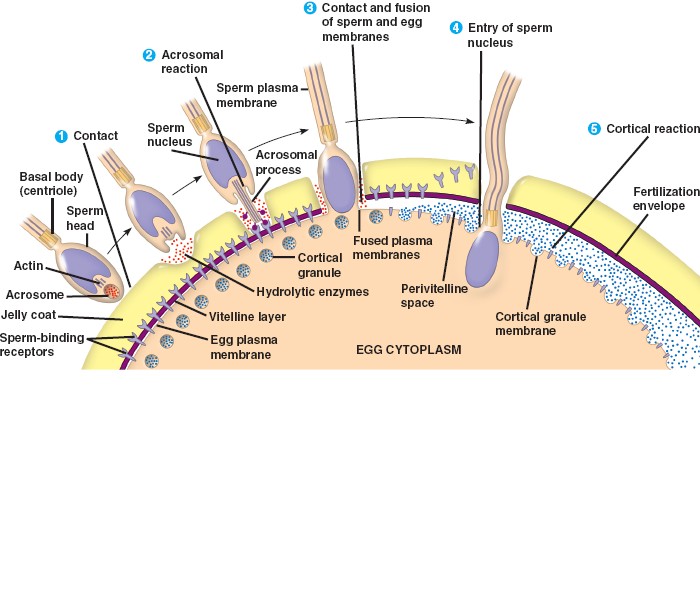
 Fertilization in sea urchin.
Fertilization in sea urchin.
- The acrosome releases enzymes to digest the
jelly coat.
- Actin filaments bind to
receptors in the vitelline layer.
- The sperm and egg plasma membranes fuse and become depolarized,
preventing polyspermy - the ability of other sperm to fertilize the egg.
- The sperm nucleus enters and fuses with the egg's nucleus.
- The vitelline layer swells to form a fertilization envelope
that also blocks polyspermy.
 Fertilization in sea urchin.
Fertilization in sea urchin.