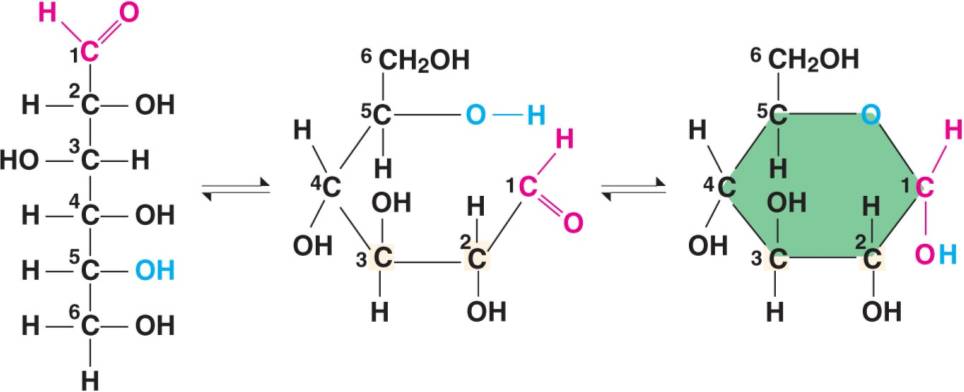
Glucose is a 6-carbon monosaccharide, or hexose.
When dissolved in water, it usually circularizes into a ring structure
where the orientation of the hydroxyl groups
on the 1 and 2 carbons result in α (alpha) and β (beta) structural
isomers.
Models of Glucose: 


