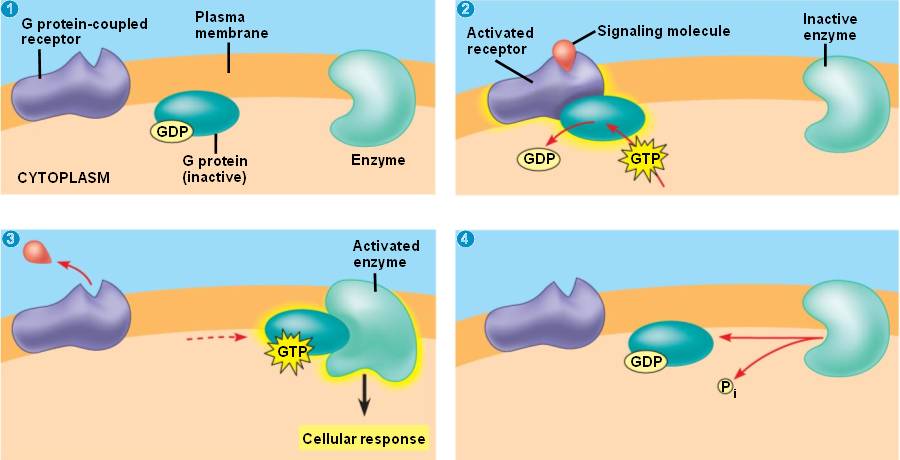
G-protein-linked receptors.
- The G-protein
is inactive when it is attached to a
GDP
(guanosine diphosphate) molecule.
- A signal molecule binds to the receptor,
which changes shape and binds to the inactive G-protein.
A GTP
molecule displaces the
GDP,
and activates the G-protein.
- The activated G-protein
binds to another enzyme
and activates it to initiate a cellular response.
- The G-protein
hydrolyzes the
GTP
and returns to an inactive state.
