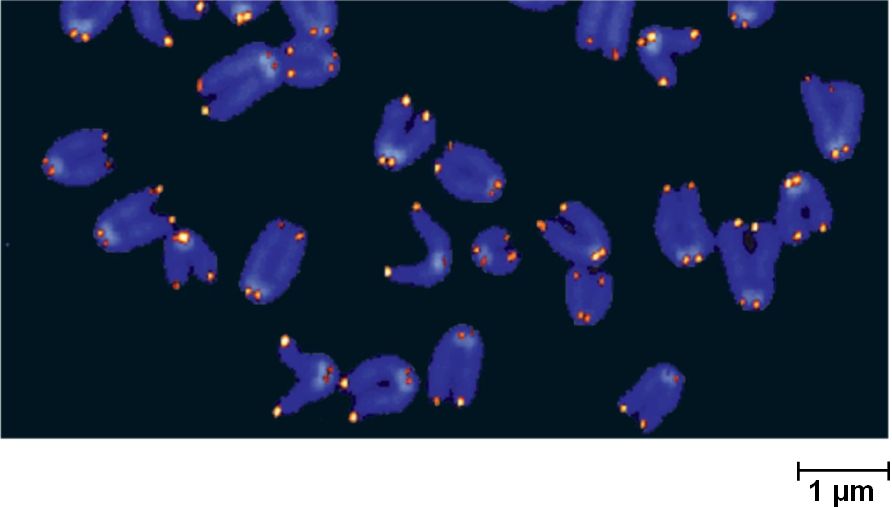
Eukaryotes have non-coding nucleotide sequences called telomeres
at the ends of their linear DNA.
The telomeres do not prevent DNA shortening,
but postpone erosion of genes near the ends of chromosomes.
Humans have a "Hayflick limit" of about 52 cell divisions before cellular death.
