
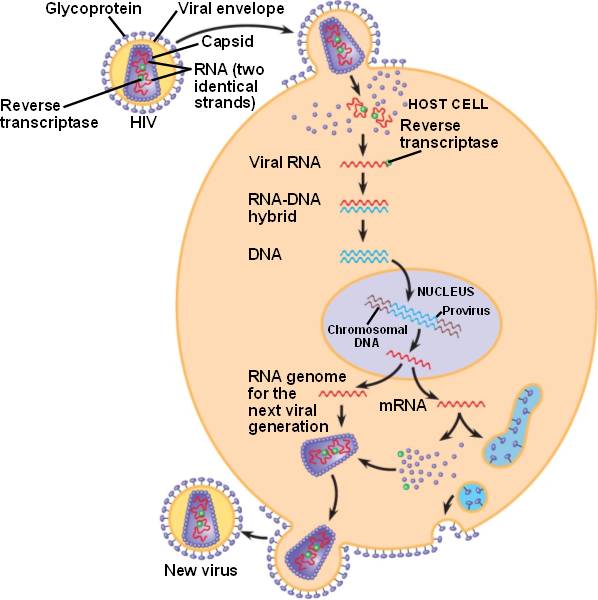
 HIV, a retrovirus.
HIV, a retrovirus.
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a retrovirus.
It has the enzyme reverse transcriptase to copy the RNA genome into DNA, which is integrated into the host genome as a provirus, where it remains a permanent resident.
The host's RNA polymerase transcribes the proviral DNA into RNA molecules, which may function both as mRNA for synthesis of viral proteins and as new viral genomes.