 Restriction enzymes.
Restriction enzymes.
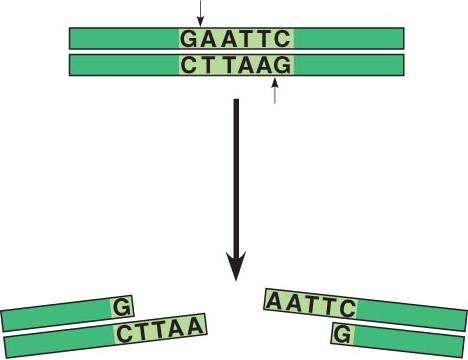
A bacterial restriction enzyme is an endonuclease that recognizes a specific DNA sequence (restriction site).
Many restriction sites are palindromes: the nucleotide sequences are the same in the two antiparallel strands.
The endonuclease makes cuts in the restriction site that leaves staggered single-stranded ends.